Imagine constructing a skyscraper without a blueprint—workers improvising floor by floor, materials arriving unscheduled, and chaos dictating progress. For decades, IT infrastructure followed a similar unpredictable pattern: manual configurations, inconsistent environments, and endless delays. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) has rewritten this story. Like a digital architect’s blueprint, IaC formalises and automates the setup of servers, databases, and networks, ensuring precision, repeatability, and speed.
In this article, we’ll explore how IaC—powered by tools such as Terraform and Ansible—transforms the way developers and DevOps teams manage infrastructure.
The Evolution from Manual Setup to Automation
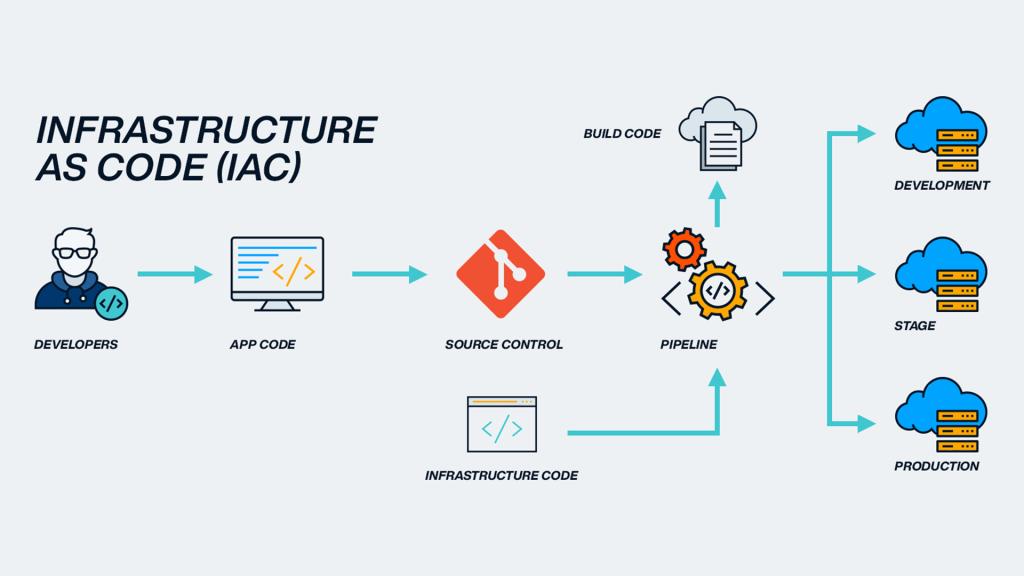
Before IaC, setting up infrastructure was like handcrafting each brick of a building—slow, error-prone, and highly dependent on the builder’s memory. Engineers spent hours configuring servers, installing dependencies, and connecting networks manually. Reproducing the same environment for testing, staging, or production often led to inconsistencies and failures.
IaC flipped this paradigm. Instead of manually assembling infrastructure, developers now describe it through code. This code acts as the single source of truth—allowing automated tools to deploy identical environments on demand. Whether provisioning ten servers or a thousand, consistency remains guaranteed.
For those aspiring to master this structured yet creative discipline, joining a full stack developer course in Pune provides practical exposure to how IaC is shaping the foundation of modern application development.
Terraform: Building Infrastructure Like an Architect
Terraform, developed by HashiCorp, is like the master architect in the IaC ecosystem. It enables developers to describe infrastructure using declarative configuration files written in HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL).
This approach means you specify what you want—a database, a load balancer, a virtual machine—and Terraform figures out how to build it. Once applied, Terraform creates a plan, previews changes, and executes them safely, ensuring environments are reproducible across teams and cloud providers.
Its true power lies in state management, which tracks deployed resources and understands differences between the desired and actual infrastructure. Terraform’s cloud-agnostic nature lets teams manage environments across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud from a unified workflow.
Just as blueprints evolve with a building’s design, Terraform configurations evolve with project needs—each update reinforcing control, not chaos.
Ansible: The Craftsman of Configuration
If Terraform is the architect, Ansible is the craftsman, ensuring every system behaves as intended. It specialises in configuration management—installing software, updating packages, and maintaining system states.
Using YAML-based playbooks, Ansible describes how tasks should be performed. Its agentless architecture means it can remotely connect to machines using SSH, execute instructions, and ensure uniformity across environments.
Ansible excels in orchestration—coordinating the sequence of steps in deploying complex applications. For example, while Terraform may create servers and networks, Ansible ensures the right versions of applications and dependencies are installed and configured seamlessly.
Together, Terraform and Ansible create an elegant balance between creation and customisation, making infrastructure provisioning as smooth as running a script.
The Advantages of Treating Infrastructure Like Code
- Version Control and Collaboration:
IaC scripts can be stored in Git repositories, enabling teams to track changes, roll back updates, and collaborate efficiently—just like developers manage application code. - Consistency and Repeatability:
Deploying identical environments eliminates the “works on my machine” problem, ensuring reliability across development, staging, and production. - Scalability and Speed:
Whether scaling up cloud instances or provisioning containers, IaC automates repetitive tasks, reducing deployment time from hours to minutes. - Reduced Human Error:
Since configurations are codified and tested, the risk of manual mistakes drastically decreases. - Cost Efficiency:
Automated infrastructure can spin up or shut down resources dynamically, ensuring optimal use of cloud budgets.
For professionals seeking to integrate these practices into real-world workflows, a full stack developer course in Pune often includes modules that combine automation, scripting, and cloud deployment—bridging theory with applied skills.
Real-World Impact and Industry Adoption
Companies such as Netflix, Spotify, and Airbnb have embraced IaC to achieve massive scalability and reliability. Their ability to spin up thousands of servers instantly or roll back faulty deployments highlights the maturity of automated provisioning.
Even small startups can benefit—automating their cloud setups to compete efficiently without heavy manual overhead. IaC also enhances disaster recovery, enabling instant recreation of environments from code repositories after system failures.
Conclusion
Infrastructure as Code represents the blueprint of the modern digital world—a bridge between human creativity and machine precision. By codifying infrastructure, organisations gain predictability, agility, and resilience, all while freeing engineers from repetitive tasks.
As automation continues to shape the IT landscape, IaC isn’t just a skill—it’s an expectation. Developers who embrace it aren’t merely writing code; they’re architecting systems that define tomorrow’s innovation. For anyone ready to step into this future, understanding IaC is the cornerstone of becoming a versatile, forward-thinking full-stack professional.